Money launderers can hide well to depict their transactions as legal. However, Datactive reveals hidden connections and patterns in data instantly, so crime rings are no longer invisible.
The main purpose of money laundering is the legalization of illegally obtained money. These illegal transactions can be the financing of terrorism, illegal arms sales, drug dealing, bribery, and even human trafficking. Financial institutions must not be a part of such transfers. All countries have a board or council to audit banks regularly as MASAK in Turkey. Therefore, departments such as compliance have to report these boards to demonstrate that they are not a part of any illegal transaction. For the detection of all organized crime members, hidden patterns must be discovered by uncovering all connections. Therefore, a comprehensive research method is necessary for such a large-scale crime.
Advanced Research for the Discovery of Digital Footprints
The main rule of financing illegal activities is to hide the source of the money and depict them as legal. At this point, criminal organization members can disguise themselves well to be invisible. However, every transaction leaves a digital footprint behind no matter how hidden it is. Even the absence of any footprint may be an indication of a suspicious person or transaction. The discovery of all these digital footprints is not possible with rule-based transaction monitoring systems. Members of criminal organizations may develop strategies to bypass the existing systems. In fact, some criminals may even be employees of the institution and are quite experienced in bypassing the system. It is a fact that money laundering organizations cannot be detected and prevented completely with existing systems or traditional methods.
Why Do Financial Institutions Fail to Prevent Money Laundering?
The legitimation of illicit money transfers is a serious threat to financial institutions. Some cases are ignored while researching this threat. One of them is the belief that rule-based transaction monitoring systems, as we have mentioned, are sufficient to detect money laundering activities. However, since these systems do not support relationship-oriented visualization of all activities on a single interface, they are insufficient in the detection of organized crime rings*. It is another mistake to consider that analysis only on transaction data is sufficient for money laundering detection. However, connection data has key importance in terms of detecting launderers who conduct their transactions hidden and indirectly*. This connection data can only be revealed by the entity-link analysis method. Finally, there is a perception that advanced analytical solutions are expensive. However, if we consider the extent of smuggling prevented by such systems, the return on investment in the system will be much higher. A comprehensive end-to-end solution allows institutions to optimize costs for preventing money laundering operations.
Consequences of Money Laundering for Financial Institutions
As we mentioned, banks that are intermediaries in such a money transfer, even indirectly, cause serious sanctions. In addition, the involvement of a bank in this type of organized crime will result in loss of reputation and customers. In this regard, the loss of money and customers also has a serious negative impact on the bank’s income ultimately.
Transactions That May Indicate Money Laundering
• Large transfers between accounts whose holders or origins are not well-known.
• High-frequency transfers between small amounts.
• Amounts that are inconsistent with the services or goods acquired.
• Money transfers to multiple different accounts in a short period.
• Transfer money to people on the sanctions list.
To bypass rule-based transaction monitoring systems, launderers make their transfers through unsuspecting accounts. These accounts can be:
Mule Accounts
Some people sell their bank accounts to organized crime rings. The owners of these accounts are not on any sanction or suspicious list. They are not detected as suspicious because they appear as a standard account.
Businesses Not Actively Operating
Businesses that have been closed can be shown as being operated. Sometimes these companies are hidden inside other large companies and can be shown as revenue-generating even though they are not operating. These businesses are not perceived as suspicious because they depict as legal.
Laundering Directly Through Active Businesses
Here, on the other hand, money is laundered by presenting the service as if it was purchased through the organizations that actively provide service. However, the amount transferred is usually not the equivalent of the relevant product or service.
Common Money Laundering Methods
Quick Money Transfers
It is a method that is carried out by transferring funds from account to account very quickly, without triggering rule-based transaction monitoring systems.
Legitimation of Money
Moving money to other actively profiting accounts is a method of depiction of money as an exchange for legitimate business.
Smurfing
It is the method of laundering that the total amount is divided and transferred over different accounts in order not to trigger rule-based transaction monitoring systems.
Online Betting/Gambling
Collecting small amounts of money under online betting or gambling in a single person who is predetermined to win.
As you can see, the money to be laundered with these methods is legitimized, and the methods are always embedded in normal transactions and designed to bypass rule-based transaction monitoring systems. Therefore, the tracking of digital footprints is only possible with an advanced intelligence system that provides entity-link visualization. Datactive analyzes the data in different data sources with a relation-oriented perspective and finds the path to the most accurate probability in the shortest time.
Which Point Should Be Considered?
The most important stage to be considered during the analysis is the stage of collecting the money. At this point, powerful network analysis capability will come into play. The account, where the money is collected, can be the trigger point for the research. This account usually has an unusual activity or relationship. Here, the simultaneity and sequences of transactions, closeness of amounts, and relationships of individuals such as family members or partnerships give clues. With the filtering features on the scenario screen and right-click actions on the schema screen, the details of the accounts and persons which are defined as entities can be expanded and more hidden connections can be revealed.
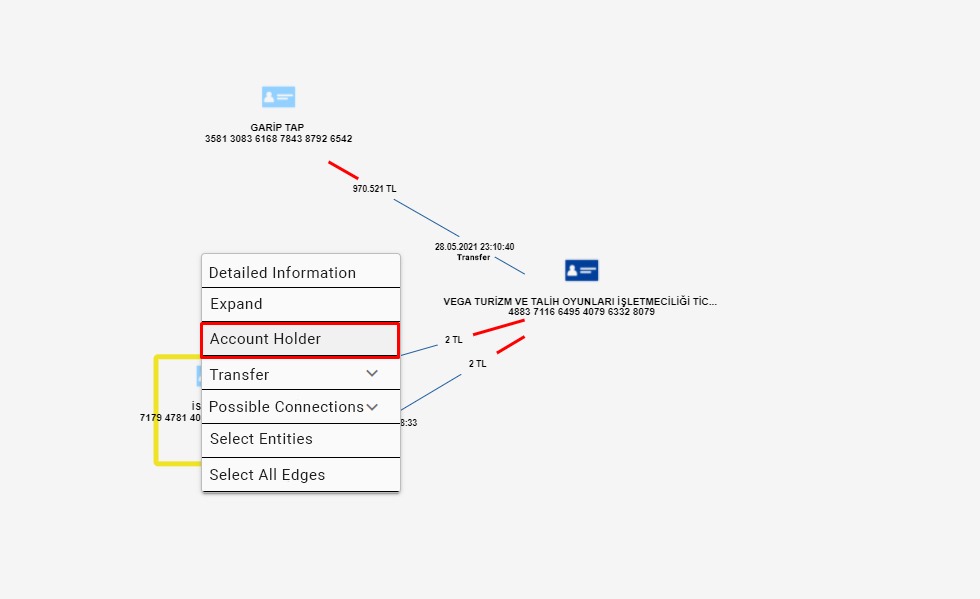
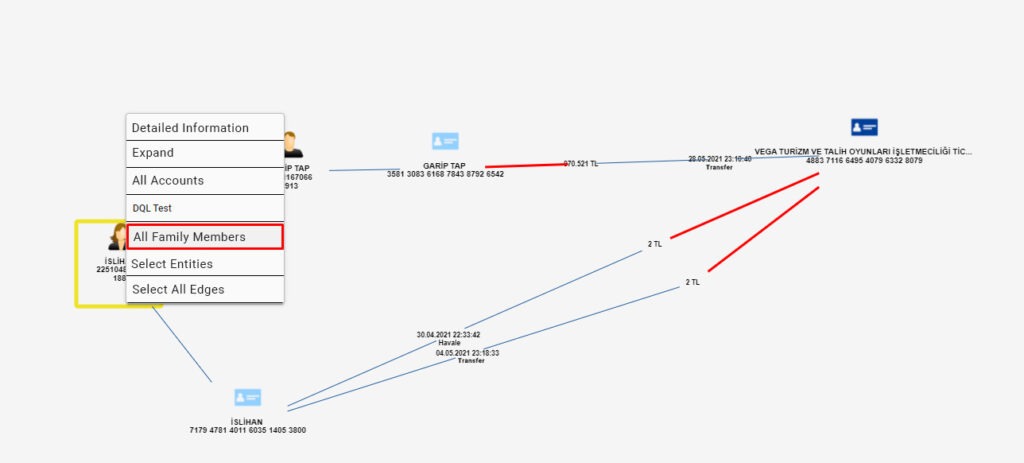
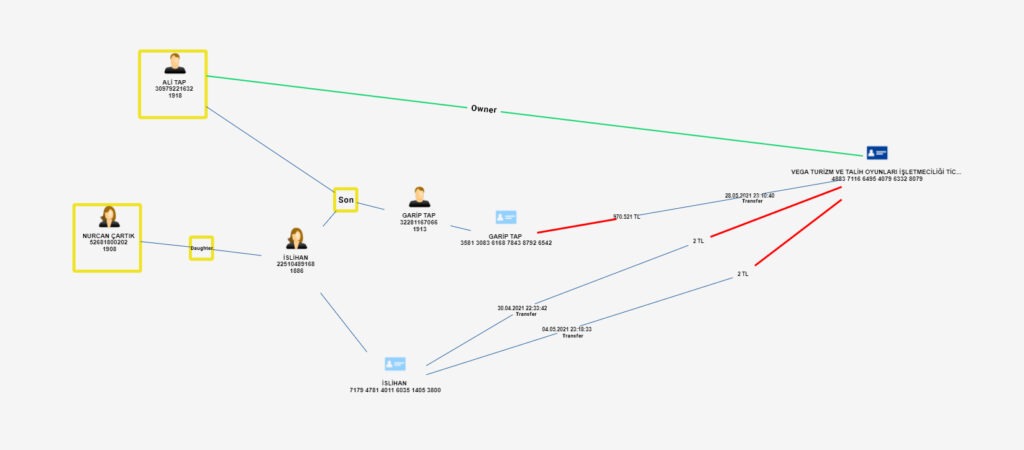
As seen in the images above, we expanded our network by using the expansion options in a seemingly ordinary process and uncovered connections that we could not see at once. Thanks to the data discovery functions, we have identified the account holders’ relationships and their connections with the account holder where the money is collected.
Fighting money laundering requires advanced research as organized crime rings have developed strategies based on bypassing the current system. Therefore, banks should be more careful since they are sanctioned if they are detected. Therefore, financial institutions need an advanced research system to combat money laundering, terrorist financing, and sanctions list violations.
